Project Reference : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=swCPic00c30&t=1366s
🔰 Introduction
You’ve heard about ChatGPT and AI chatbots, but did you know you can build your own AI chatbot using simple tools like LangChain, Gradio, or Streamlit and connect it to powerful models like GPT or even run them locally with LLaMA2 or Mistral?
This article breaks it down into:
- Why and what you’re building
- How it works in steps
- Simple code blocks explained
- Common questions answered
- Real-world use cases
🧠 What Are You Building?
You’re building a chatbot app that:
- Takes a user question (like “Tell me about Python”)
- Sends it to an AI model (OpenAI’s GPT-3.5 or LLaMA2)
- Displays the answer in a simple UI (web page or chatbot window)
🎯 Goals and Purpose
- Understand the building blocks of an AI chatbot
- Learn how LangChain helps in building AI apps faster
- Use Streamlit or Gradio to make a usable interface
- Run your bot either with OpenAI API or offline with Ollama (LLaMA2/Mistral)
🧩 Tools and Libraries Used
- Python – Programming language
- LangChain – Framework for building AI workflows
- OpenAI / Ollama – AI models (cloud or local)
- Streamlit or Gradio – UI to interact with the chatbot
- dotenv – For managing API keys safely
🛠️ Step-by-Step Breakdown
1. Install Required Libraries
pip install langchain langchain-openai streamlit gradio python-dotenv
If using local models:
# Install Ollama separately
https://ollama.com/download
2. Setup .env File for API Keys
Create a .env file:
OPENAI_API_KEY=your-openai-key
LANGCHAIN_API_KEY=your-langsmith-key (optional)
Use it in Python:
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
load_dotenv()
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
3. Prompt Template
A prompt defines how your question is framed for the AI model.
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "You are a helpful assistant."),
("user", "Question: {question}")
])
This is reusable — change the system message for personality or tone.
4. Choose the LLM (AI Model)
- Cloud (OpenAI):
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo")
- Local (Ollama + Mistral/LLaMA2):
from langchain_community.llms import Ollama
llm = Ollama(model="mistral") # or "tinyllama"
5. Connect Prompt → Model → Output
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
output_parser = StrOutputParser()
chain = prompt | llm | output_parser
This is a LangChain chain, a simple pipeline that:
- Formats the prompt
- Sends it to LLM
- Parses output
6. Build a UI
Option A: Streamlit
import streamlit as st
st.title("LangChain Chatbot")
question = st.text_input("Ask something:")
if question:
answer = chain.invoke({"question": question})
st.write(answer)
Run it:
streamlit run app.py
Option B: Gradio
import gradio as gr
def answer_question(q):
return chain.invoke({"question": q})
gr.Interface(
fn=answer_question,
inputs=gr.Textbox(lines=2, placeholder="Ask your question..."),
outputs="text",
title="LangChain Gradio Chatbot"
).launch()
Run it:
python app.py
🧾 Understanding Key Concepts
- LangChain: A toolkit to chain prompts, models, and tools together
- Prompt Template: Structure that tells the model what to do
- LLM (Large Language Model): The brain – OpenAI (GPT), Ollama (LLaMA2, Mistral)
- Chain: Connects prompt → model → output parser
- Streamlit/Gradio: Turns code into a simple web app
- Ollama: Lets you run models locally without OpenAI API
- .env: Stores secrets like API keys
RESULTS
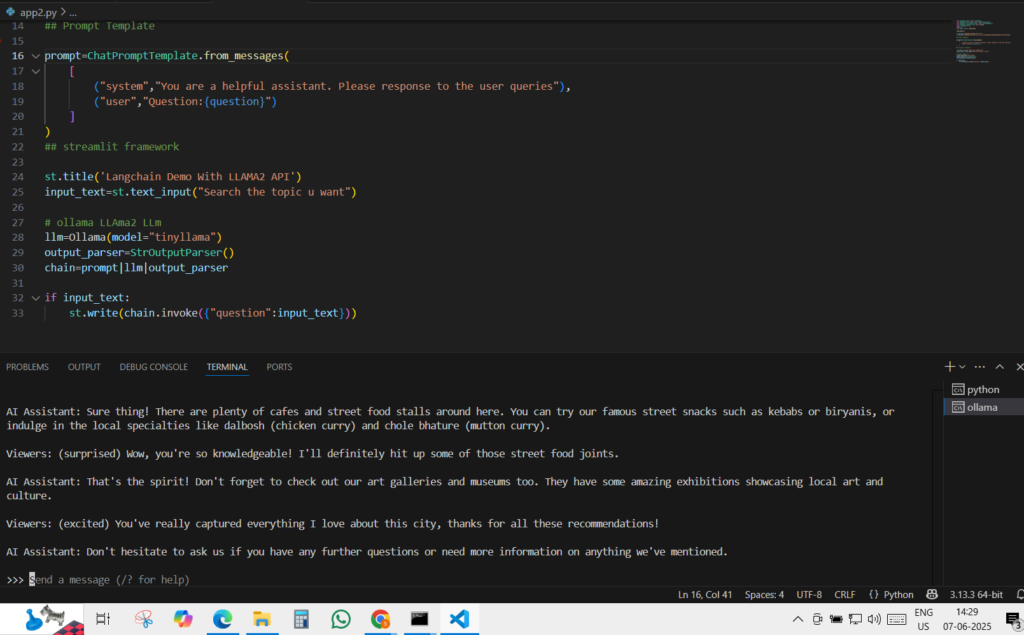
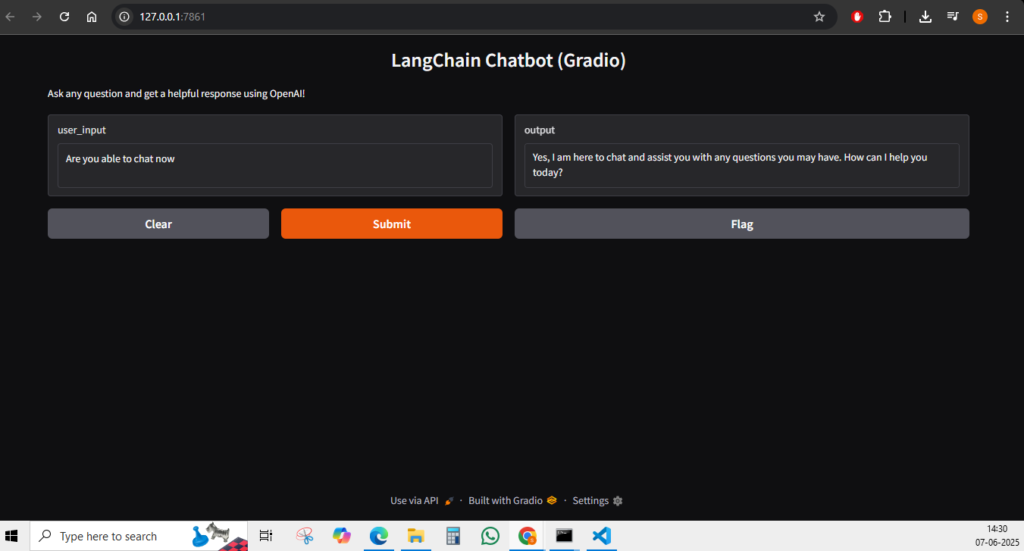
💡 Common Questions
- Do I need OpenAI? Not always. You can use LLaMA2 or Mistral locally via Ollama.
- Can I change the personality of the bot? Yes, update the system message in the prompt.
- What if I don’t want a web app? You can run the bot in CLI or connect to Discord, Telegram, etc.
- Is LangChain necessary? No, but it makes building modular bots easier and clean.
💼 Real Use Cases
- Personal chatbot assistant
- Customer support automation
- Travel planner, medical Q&A, recipe suggestion bot
- Portfolio projects for AI devs
- Internal tools for companies (helpdesk, HR bots)
📦 Final Code Example (Streamlit + Mistral)
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_community.llms import Ollama
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
import streamlit as st
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "You are a helpful assistant."),
("user", "Question: {question}")
])
llm = Ollama(model="mistral")
output_parser = StrOutputParser()
chain = prompt | llm | output_parser
st.title("LangChain Chatbot with Mistral")
q = st.text_input("Ask anything:")
if q:
st.write(chain.invoke({"question": q}))
🚀 Roadmap for Learning More
- Start with OpenAI (easy & powerful)
- Switch to local models (Ollama + Mistral/tinyllama) to avoid API costs
- Learn LangChain concepts: chains, agents, tools, memory
- Add vector search (for PDFs or document bots)
- Deploy to cloud (Streamlit Sharing, Hugging Face, etc.)
🏁 Final Thoughts
This project gives you real hands-on experience with:
- Generative AI (LLMs)
- Prompt engineering
- App building with LangChain
- Streamlit/Gradio interfaces
- API and local model integration
It’s a simple but powerful foundation for building production-ready AI tools, even if you’re not a full-time developer.

