Introduction
In this article, we’ll explore how to build a Q&A chatbot using LangChain, OpenAI, and Gradio. We’ll cover:
- Setting up the environment
- Creating a simple chatbot
- Debugging common errors
- Transitioning from Streamlit to Gradio
This guide is based on real troubleshooting steps, making it ideal for beginners and intermediate learners.
1. Understanding the Goal
We want to build a chatbot that:
✅ Takes user questions
✅ Sends them to OpenAI’s GPT-3.5-turbo
✅ Returns AI-generated answers
Tools Used
- LangChain (for AI workflow)
- OpenAI (for the LLM)
- Gradio (for the web interface)
- Python (for scripting)
2. Initial Setup & Common Errors
A. Installing Dependencies
First, install the required libraries:
pip install langchain-community gradio python-dotenv openaiB. Setting Up OpenAI API Key
Create a .env file:
OPENAI_API_KEY=your_api_key_here
Load it in Python:
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv() C. Choosing the Right Model
⚠️ Common Mistake: Using OpenAI() instead of ChatOpenAI() for GPT-3.5-turbo.
✅ Correct Approach:
from langchain_community.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
llm = ChatOpenAI(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo",
temperature=0.5,
openai_api_key=os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
)3. Building the Chatbot
A. Simple Q&A Function
def get_response(question):
response = llm([HumanMessage(content=question)])
return response.contentB. Creating a Web Interface
Option 1: Using Streamlit (Simple but Limited)
import streamlit as st
st.text_input("Ask a question", key="question")
if st.button("Submit"):
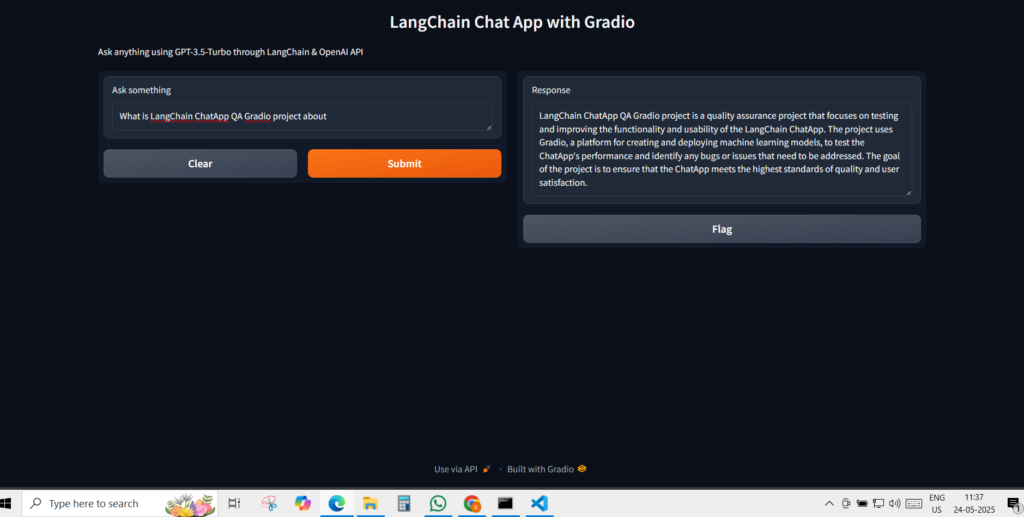
st.write(get_response(st.session_state.question))Option 2: Using Gradio (More Flexible & Interactive)
import gradio as gr
def respond(question):
return get_response(question)
gr.Interface(
fn=respond,
inputs=gr.Textbox(label="Ask anything"),
outputs=gr.Textbox(label="AI Response")
).launch()✅ Why Gradio is Better?
- Supports chat history
- Easier to customize UI
- Built-in API endpoints
4. Debugging Common Issues
| Error | Solution |
|---|---|
ModuleNotFoundError | pip install missing_package |
OPENAI_API_KEY not found | Check .env file |
Streamlit not working | Run with streamlit run app.py |
Gradio not launching | Use app.launch(server_port=7861) if port is busy |
5. Key Learnings
A. LangChain Basics
- Use
ChatOpenAIfor chat models (GPT-3.5, GPT-4) HumanMessagefor user inputsload_dotenv()for secure API key management
B. Gradio vs. Streamlit
| Feature | Gradio | Streamlit |
|---|---|---|
| UI Customization | ✅ High | ❌ Limited |
| Chat Support | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| Deployment | ✅ Easy | ✅ Easy |
| Real-time Updates | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
C. Best Practices
✔ Always handle API errors
✔ Use environment variables for API keys
✔ Test models separately before UI integration
6. Final Working Code (Gradio Version)
import gradio as gr
from langchain_community.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
load_dotenv()
llm = ChatOpenAI(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo",
temperature=0.5,
openai_api_key=os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
)
def respond(question):
response = llm([HumanMessage(content=question)])
return response.content
gr.Interface(
fn=respond,
inputs=gr.Textbox(label="Ask anything"),
outputs=gr.Textbox(label="AI Response"),
title="AI Chatbot"
).launch()7. Conclusion & Next Steps
✅ Built a functional AI chatbot
✅ Learned LangChain + OpenAI integration
✅ Compared Gradio vs. Streamlit
Next Steps:
➡ Add chat memory (for multi-turn conversations)
➡ Deploy on Hugging Face Spaces
➡ Experiment with other LLMs (Llama 3, Claude, etc.)
Final Thoughts
This journey covered real-world debugging, best practices, and UI choices. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced developer, these concepts will help in building better AI applications.
🔗 Try it yourself and share your results! 🚀